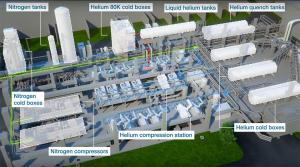
How does the ITER cryoplant work?
Designed and manufactured by Air Liquide, the ITER cryoplant includes three helium refrigeration units, two nitrogen refrigeration units and 1.6 kilometres of cryogenic lines connecting the plant to the Tokamak Building. Installation activities are underway now.
The complex workings of the ITER cryoplant are explained in this video, produced by Air Liquide.
For more on Air Liquide's contribution to ITER cryogenics, visit this page.