The TOKAMAK
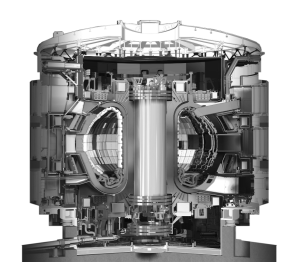
The TOKAMAK
A tokamak is an experimental machine designed to harness the energy of fusion. ITER will be the world's largest tokamak, with a plasma radius (R) of 6.2 m and a plasma volume of 840 m³.

Magnets
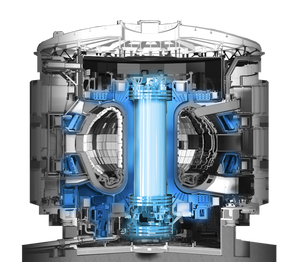
Magnets
Ten thousand tonnes of superconducting magnets will produce the magnetic fields to initiate, confine, shape and control the ITER plasma.

Vacuum Vessel
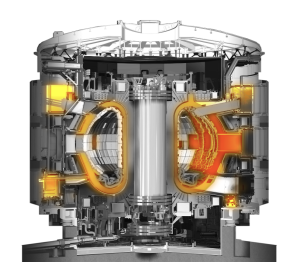
Vacuum Vessel
The stainless steel vacuum vessel houses the fusion reactions and acts as a first safety containment barrier.

Blanket

Blanket
The blanket shields the steel vacuum vessel and external machine components from high-energy neutrons produced during the fusion reaction.

Divertor
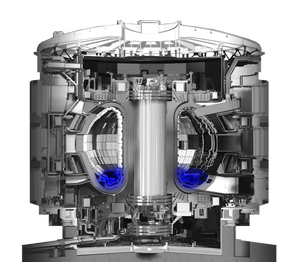
Divertor
Positioned at the bottom of the vacuum vessel, the divertor controls the exhaust of waste gas and impurities from the reactor and withstands the highest surface heat loads of the ITER machine.

Cryostat
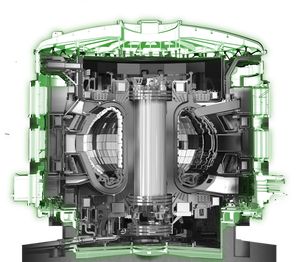
Cryostat
The stainless steel cryostat (29 x 29 m) surrounds the vacuum vessel and superconducting magnets and ensures an ultra-cool, vacuum environment.

