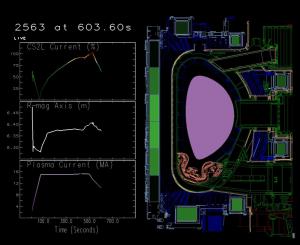
A vision of the future
RBDS is part of the high performance networking (HPN) project that ITER partly contracted in 2009 to General Atomics, the private company that operates the DIII-D Tokamak. The project investigates and prototypes technologies for data transport architecture—a key issue in tokamak operation.
On the ITER side, working on RBDS has created strong ties between CODAC engineers and Fusion Science & Technology (FST) physicists—something Anders considers essential to the success of the project.
"There are several scientists in the Member countries doing plasma simulation," says Thomas Casper, the FST experimental physicist who participated in the project. "Soon, we'll make our visualization and data system available to them. It's part of the ITER philosophy: this huge project should drag in what was scattered until to now."