Progress on ELISE
11 Mar 2011
-
Ron Hemsworth, ITER Neutral Beam Section
The photograph shows the participants at the meeting inside the shielding in front of the main insulator of the 60 kV accelerator.
The most powerful heating system to be installed in ITER will be the neutral beam injection system which is designed to inject 33 MW of high energy (1 MeV) deuterium atoms into the ITER plasma from two heating neutral beams.
The beams are made by neutralizing 1 MeV beams of D-, the negative ion of deuterium, which are created by extracting D- from an ion source and accelerating the ions electrostatically through apertures in grids held at successively higher negative potentials. Thus the ion source is at the origin of the neutral beam and a key component of the injector.
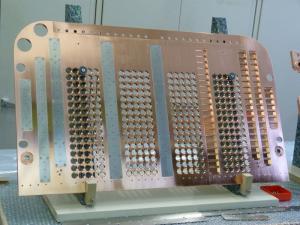
One of the two segments of the plasma grid viewed from the accelerator side. The ions are extracted from the ion source through the circular apertures.
For the heating neutral beams, ITER has chosen to further develop the radio frequency- (RF-) driven negative ion source developed at the Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP) at Garching, near Munich in Germany. The ITER ion source will be about eight times larger than the RF-driven sources developed at IPP. The next step in the development of the ion source is to build a source half the size of that of ITER, and to test its performance on the "Extraction from a Large Ion Size Experiment" (ELISE) test bed that is now under construction at IPP.
ELISE aims to extract and accelerate to 60 keV 20 A of D- for 3,600 s—half the current, but the full pulse length that will be required from the ITER source. The status in the construction and design of ELISE was the topic of the progress meeting held on 3-4 March at IPP with the participation of staff from ITER, IPP, the European Domestic Agency F4E and the RFX Consortium from Padua, Italy.
The large vacuum tank, gate valve and the main insulator of the accelerator have been delivered to IPP and are installed inside the specially constructed biological shield that is needed around the test bed to protect the scientists and engineers from radiation generated by the beams. The main parts of the ion source and the grids of the accelerator have also been delivered to IPP, but they still need to have the molybdenum coating applied to the surfaces that will be "seen" by the plasma inside the ion source.
Some technical difficulties have led to a delay of about four months in the procurement program, and it is now expected that the installation will be completed, and commissioning will start, in January 2012. The success of ELISE will greatly reduce the risk associated with the final development of the full-size ITER ion source at the SPIDER test facility at RFX, Padua.