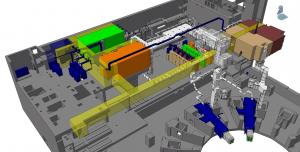
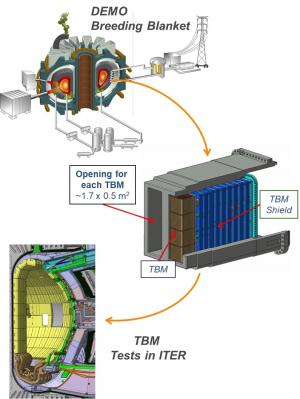
"I think of the test blanket modules as the tip of the iceberg," says Merola. "Behind the steel boxes are enormous ancillary systems." Some of these systems will extract the tritium, process it, and account for it. Others will remove the heat and channel it to where it can be used to demonstrate the feasibility of generating electricity in a future fusion power plant. Still other systems will purify the coolant and take measurements to monitor the test blanket systems, and collect essential data that can be extrapolated to help in designing DEMO blankets.
The four different test blanket systems (module plus ancillary systems) that will be installed in ITER will be used to test different combinations of design options: a liquid metal breeder versus solid breeders, and helium coolant versus water coolant.
The liquid breeder is lithium-lead, which becomes liquid at 235 °C. The main advantage of this breeder is that it can be refueled during operation. But a challenge is that liquid breeders interact with the magnetic fields. To overcome this problem, the lithium-lead has to either flow at a low velocity or be electrically isolated from the metallic walls.
Solid breeders do not interfere with magnetic fields, but they cannot be refilled online. Instead, they have to be replaced from time to time—an operation that requires the reactor to be stopped so the exhausted breeder can be replaced.
As far as coolants go, water has the advantage of being well known through years of use in fission reactors. But water has one big disadvantage when it comes to extracting heat: without high pressure, water cannot be raised to the temperatures needed for efficient conversion between thermal and electric energy. Helium, on the other hand, can be brought up to 500 to 600 °C, but it has the disadvantage of a much lower heat capacity. To compensate, a higher flow velocity is required, which means higher pumping power.
Improving the models to inform future designs
Simulations can be used to predict the behaviour of the test blanket systems, but the models underpinning the simulations have to be validated through a set of experiments. These experiments on ITER will also help to further understand the parameters that can be used to tune the breeding process. "There are different ways of tuning the efficiency of tritium production," says Merola. "For example, altering the density of the breeding material or using neutron multipliers. There are also different ways of tuning the process of extracting the tritium, of separating it from other gases, and of re-injecting it into the plasma."
The ITER TBM Program will test the test blanket systems separately in order to determine the advantages and drawbacks of each concept. The program will also gain experience over the years to help determine which components need to be replaced, and how often. "These are all things that are not yet fully understood, because there is no breeder blanket tokamak anywhere in the world," says Merola. "We will be on the front line of fusion research, taking an essential step towards DEMO."
*DEMO: the general term for next-phase DEMOnstration fusion reactor projects. Different conceptual DEMO projects are under consideration by all ITER Members.