Magnetic island reflects microwaves
Researchers from the Dutch Plasma Physics Institute Rijnhuizen, together with colleagues from Denmark and Germany, have discovered that so-called magnetic islands in fusion reactors can reflect microwaves. Their result was published in Physical Review Letters of 15 September 2009.
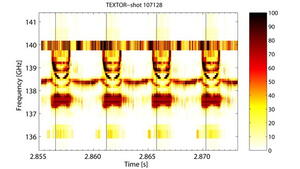
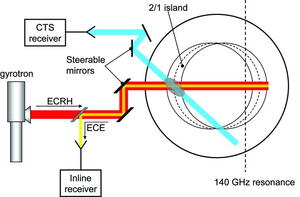
Magnetically-confined plasmas for nuclear fusion research exhibit a number of instabilities. One class of these are the so-called magnetic islands, which can destroy the confinement. One way of controlling these islands is by heating them at exactly the right spot with a beam of microwaves. During experiments on the German TEXTOR fusion experiment, the Rijnhuizen researchers discovered a previously unknown phenomenon: under certain conditions, the islands reflect part of the microwaves.
With a clever use of limited resources, a dedicated diagnostic system was designed and built to characterize the effect. The details of this system will soon be published in a Review of Scientific Instruments paper.
According to the measurements, the reflection of microwaves strongly depends on the heating power and the density of the plasma. To get a better understanding of the phenomenon, further experiments on the German Asdex Upgrade tokamak are planned. These experiments will indicate whether or not designers for the international ITER experiment should take the reflections into account. It is possible, though not expected, that the reflected beams blind delicate diagnostics installed on ITER.
Reference: Strong Scattering of High Power Millimeter Waves in Tokamak Plasmas with Tearing Modes, Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 125001 (2009).