Final design review of ITER's in-wall shielding
Last week the final design review for the ITER vacuum vessel's in-wall shielding was held in Cadarache. Experts from the ITER Organization, Europe, Korea, Russia and India participated in this meeting that was chaired by Brad Nelson from the US Domestic Agency. Participants discussed the design of the shields and identified outstanding issues that needed to be finalized before signing of the Procurement Arrangement, which is scheduled to happen next month.
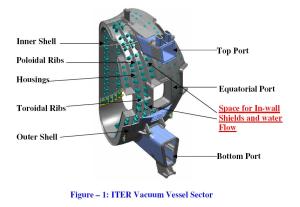
The in-wall shielding for the ITER Tokamak is composed of modular blocks made of borated and ferritic stainless steel plates that fill the space between the double walls of the vessel structure. The main function of these inserts is to provide neutron shielding and to reduce field ripple. Water flow channels provide the cooling of the material.
Field ripple along the outer edges of the plasma can produce potentially damaging hot spots to the first wall. This effect can be reduced by increasing the size or number of toroidal field coils or by installing ferromagnetic inserts between the plasma and the toroidal field coils. Due to cost and space restraints, the use of ferromagnetic steel plates looks like the most viable solution. Five different materials will be used in ITER: for the neutron shielding steel of types 304B4 and 304B7 has been chosen, and for the ferromagnetic inserts chromium stainless steel plates of type 430.
The Indian Domestic Agency will fabricate and deliver more than 6,000 shielding blocks for installation into the vacuum vessel sectors in Korea and Europe, while some blocks will be delivered to ITER for installation in the field joints regions when the vacuum vessel sectors are assembled at Cadarache. The weight of each neutron shielding plate can vary between 50 and 500 kg with an average size of 50 cm x 20 cm x 43 cm depending on its location.
Other topics discussed in this final design review ranged from risk assessment, scheduling and manufacturability to physics considerations including electromagnetic analysis structural analysis and neutronics.
A report based on findings by the design review board members will shortly be presented to ITER.